How to use Critical Path Method in activity network diagram or PERT

In a project for showing all the sub tasks, activity network diagram is an important method, which is used for displaying the timelines of different sub tasks.
During the project there are number of question like
- How much time a Project take for completion?
- How much time has been taken by the entire sub task separately?
- Which tasks are completed at a time?
- Which are the critical tasks, which can take extra time for completion?
By the use of activity network diagram, total time for the completion of the task, starting time of each task, ending time of each task are calculated and displayed with the graphical methods. The critical path method (CPM) was invented in the late 1950’s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley, Jr. of Remington Rand.
Critical Path Method helps to identify the longest possible path for the completion of project.
Activity network diagram is also common to project managers by the name Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) or Critical Path Diagram. By use of the activity network diagram, we can able to determine that which activity take more time or we can say that which activities time is consuming. So by knowing about the time consumable by all the activities it is easy to determine that on which activity there is a need to apply more stress or on which activity need to apply less stress. So that whole project can be completed on time. As in an activity network diagram time, of all the activities are determined so creating an activity network diagram is a time consuming process.
In the project bounding, critical path method has an important role. Let’s see how it works:
Right Team: For Completion of the project at right time team has a great role. All the team members must have a knowledge about the all the sub tasks which are performed for completion of the project. Team will consist of manager, team members etc. For completion of the Project.
Main Subtask: Try to complete main sub task of the project first. Main sub task means those task without which project cannot be completed. For this purpose take the reference of the previous project, check out what were the main sub task for the completion of the project. As a reminder write the task at the top half on the activity card.
Arrange all the activity tasks in a specific order – which are required for completion of the entire project smoothly. For connection of all the activity cards use the path, which make a sequence for complete the whole project. If at any time, there is a requirement of new activity card it is easy to insert in sequence and if any activity card did not require, it can be easily deleted.
Time Duration: Assign the time duration of the each task for the completion and write it on the bottom half of the activity card. Check those activity cards have hours, minutes, and days for the completion. So select these cards which require less time for completion.
Determine Critical Path: Calculate the completion time of the all sub tasks so that we can able to determine the total time required for completion of project. The path which is used for the completion of all the sub tasks is known as Critical Path. By the critical path it is easy to check that project is going on a pre-define schedule or not. It is helpful for making the improvement in the speed of the completion of the project. Here, one important aspect is that if we can reduce the time/schedule for critical path, the project can be completed in less time. Basically, the critical path can help in determining possibilities of increasing the speed.
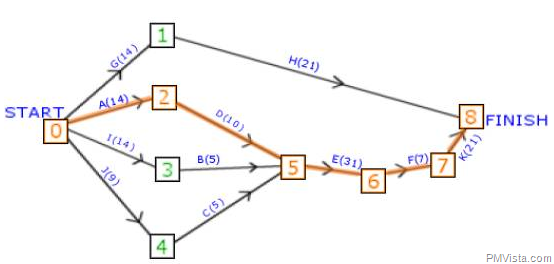
At the end calculate the earliest starting time and the finishing time and also calculate the latest starting and finishing time for all the subtasks which are helpful for the completion of whole Project.
Comments
| Tweet |
|